DQL definition and basic queries
This subsection mainly illustrates DQL definition and basic queries with DQL.
Suppose you want to query data in the above composite table emps.ctx. Let’s look at how DQL perform dynamic queries through simple operations in the interface without having to know the database table’s structure. It is simple, only several steps are enough to get it done effortlessly.
As you have learned how to define a pseudo table in the previous chapter and make the data source ready, let’s move on to create a metadata file using the defined pseudo table and then explain the uses of the DQL model in DQL queries.
Step1: Generate DQL table from pseudo table
Open demo.glmd where the pseudo table is defined in Metadata Editor. First, generate a DQL table by clicking Tool - Generate table from pseudo table:

All potential pseudo tables are automatically selected in the pop-up window.
All fields and special fields under “Field” are automatically checked, such as emps shown above.

Click “OK”:
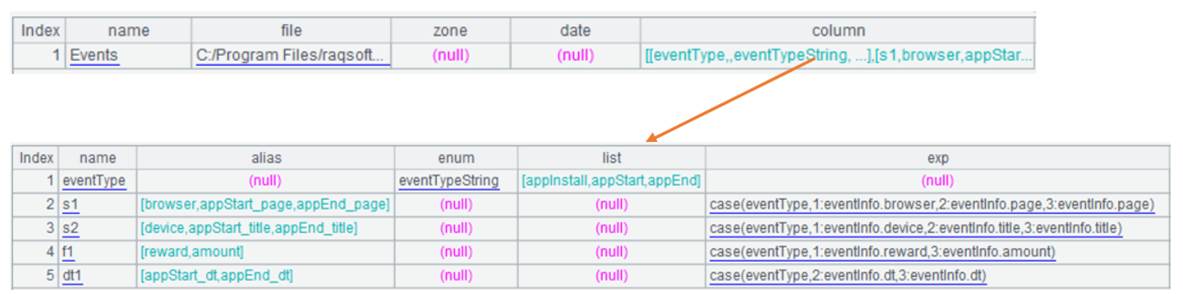
Click “Save” to finish creating the DQL table for the metadata file. The more complicated metadata definition will be illustrated later.
Step 2: Perform simple DQL query
Now we can perform a DQL query. Click Tool - DQL query:
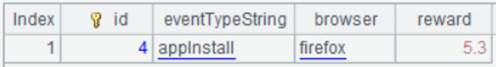
Double-click table name emps and the DQL query statement will be automatically displayed in the edit box. By default, all fields, including the pseudo fields, in the table will be queried.
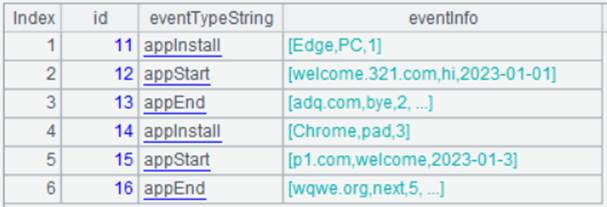
Click “Execute” button to view the query result:
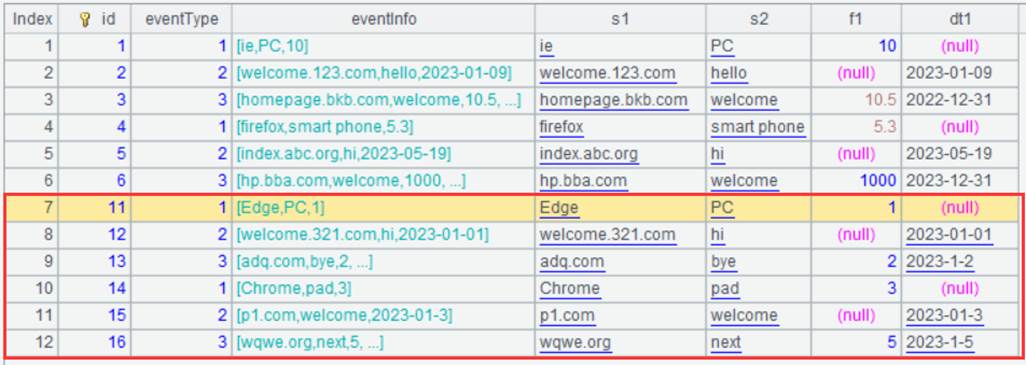
You can also query data of certain fields by checking the corresponding fields under Select.
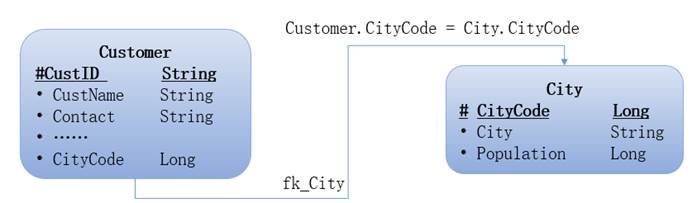
See Join query syntax to for writing custom query statements.